Derived from the Aspergillus genus, aflatoxins, commonly from the Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus species, are found across the globe and result in an estimated 25% of the world’s food crops being destroyed annually. This specific toxin is often categorized as a ‘storage toxin’ since it typically occurs when the grain is exposed to excess moisture and heat during storage and/or transportation. Aspergillus molds are typically found in corn, cottonseed, barley, rice, and oats.
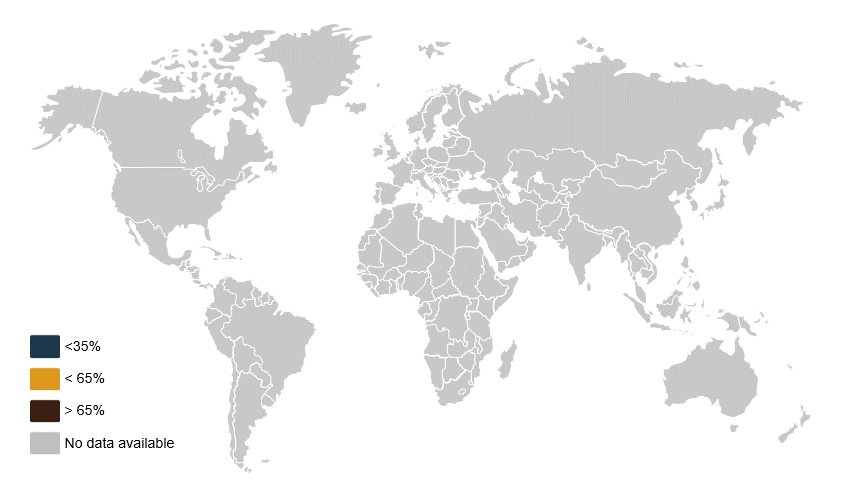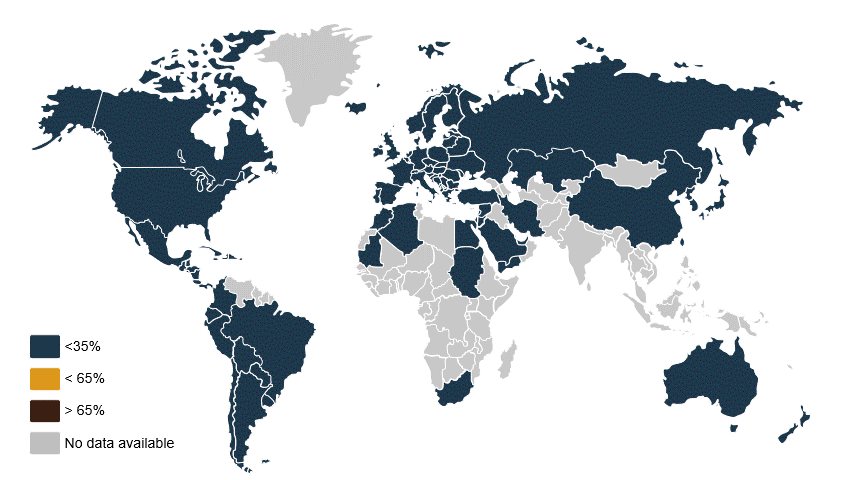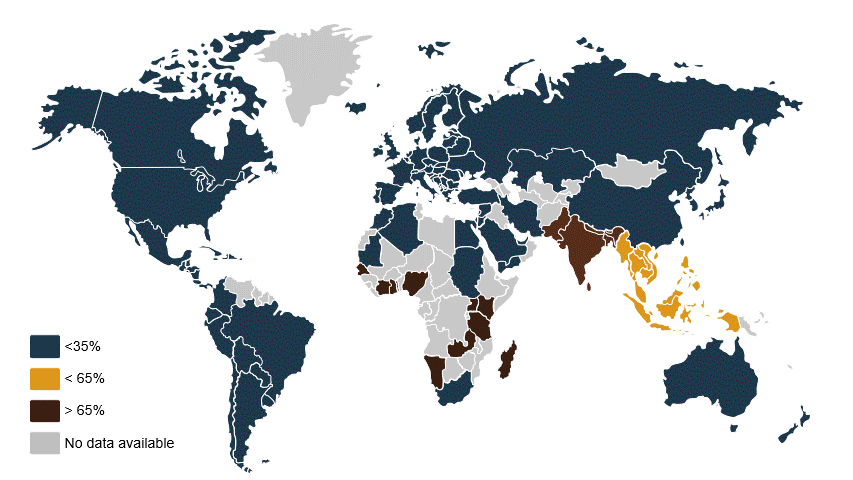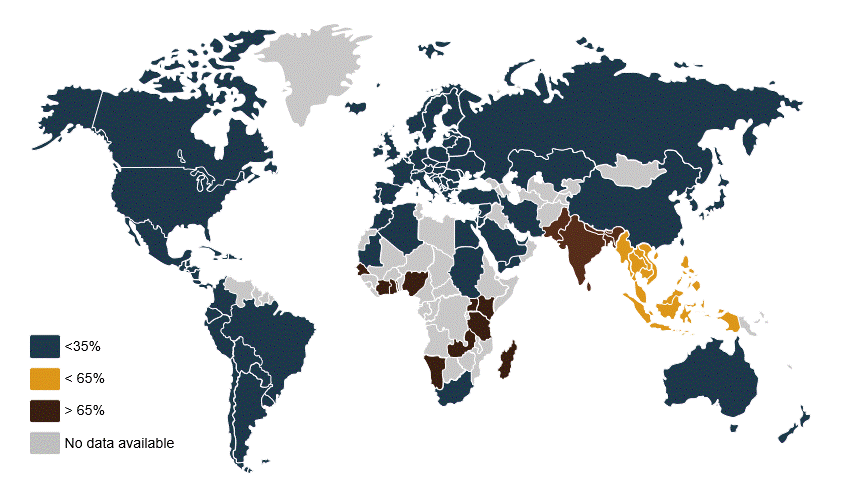
Abundant in tropic and subtropical regions with high temperatures and high humidity, aflatoxins are considered one of the most potent mycotoxins with carcinogenic traits impacting animals and humans. It is present in grains throughout the world and often transported globally. Aspergillius’ ability to grow in storage makes monitoring and preventing its harmful effects imperative to the food industry.

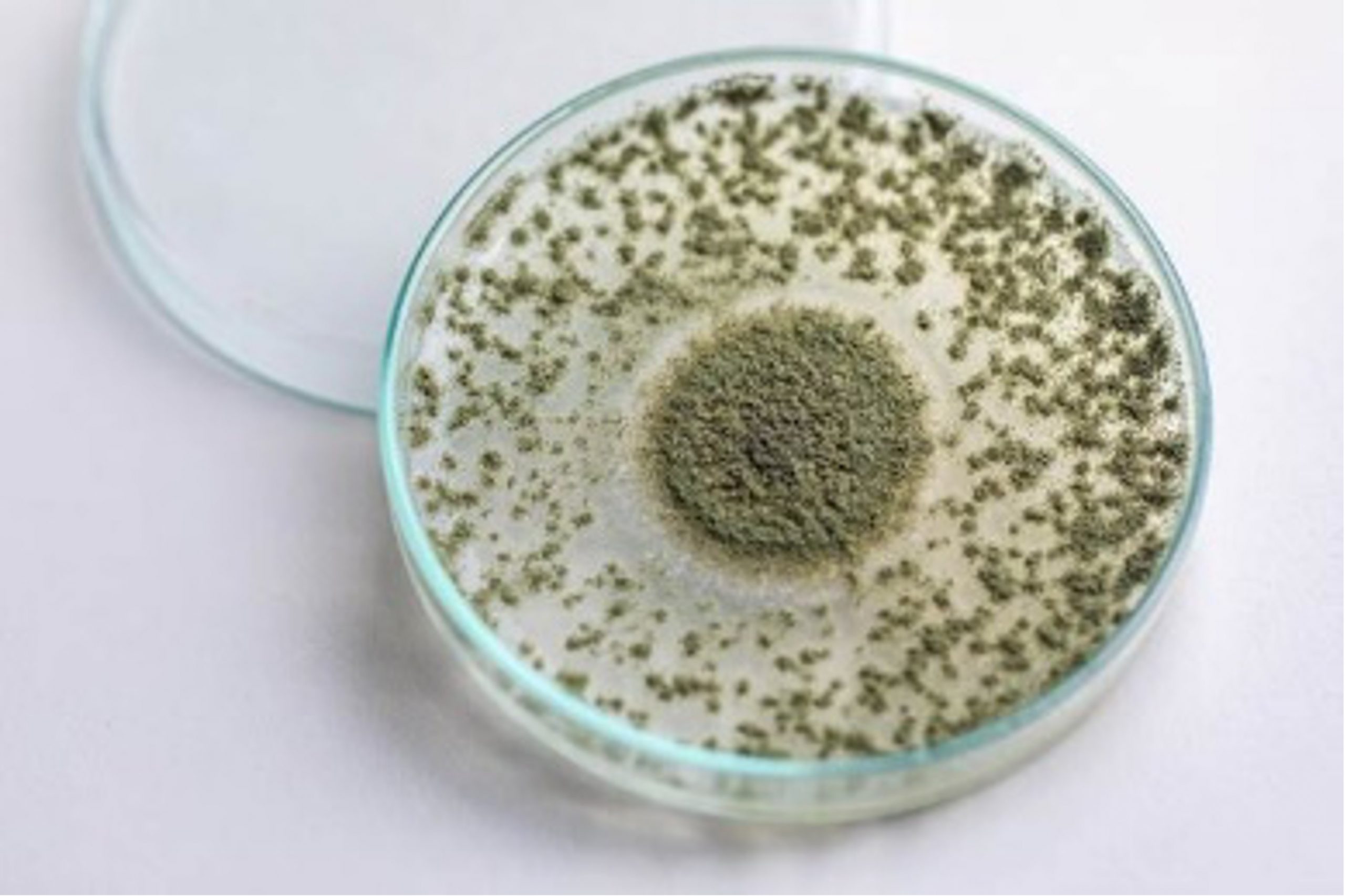
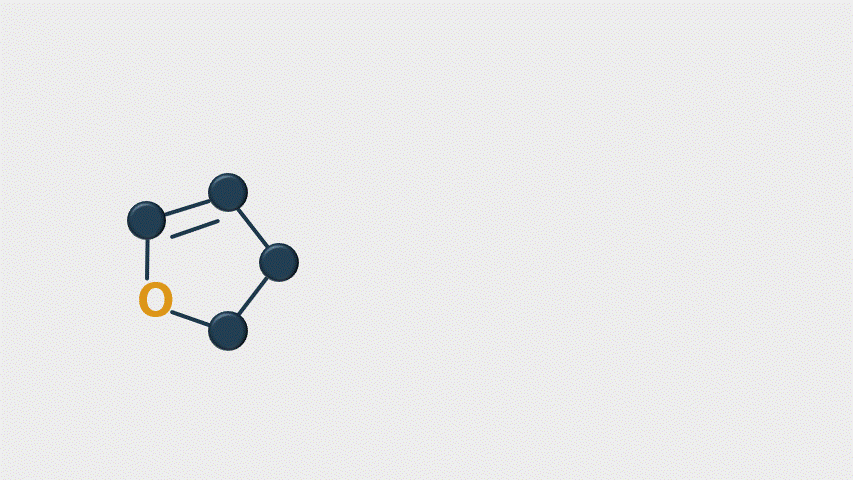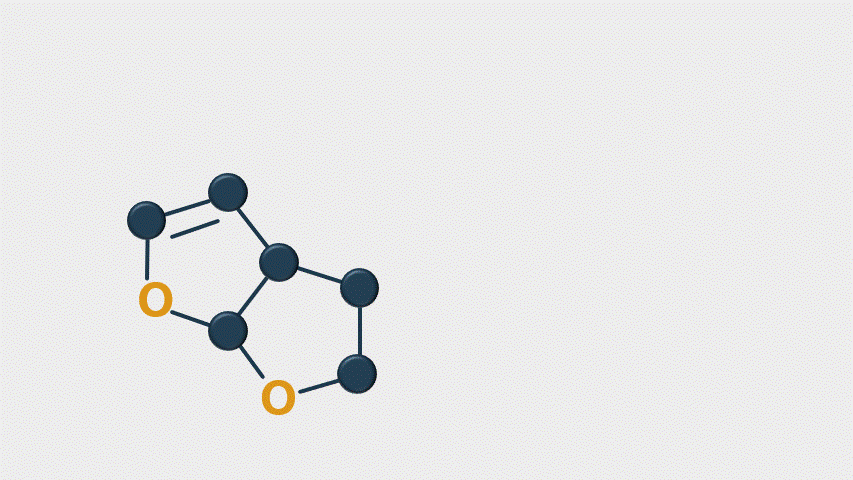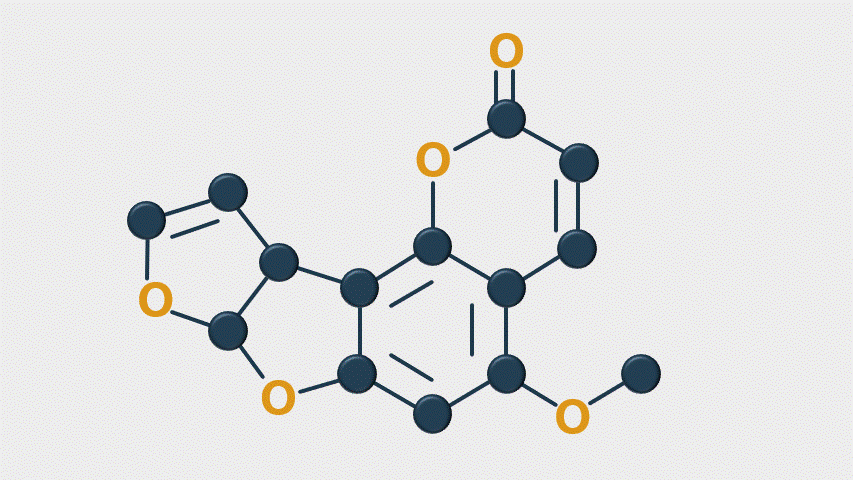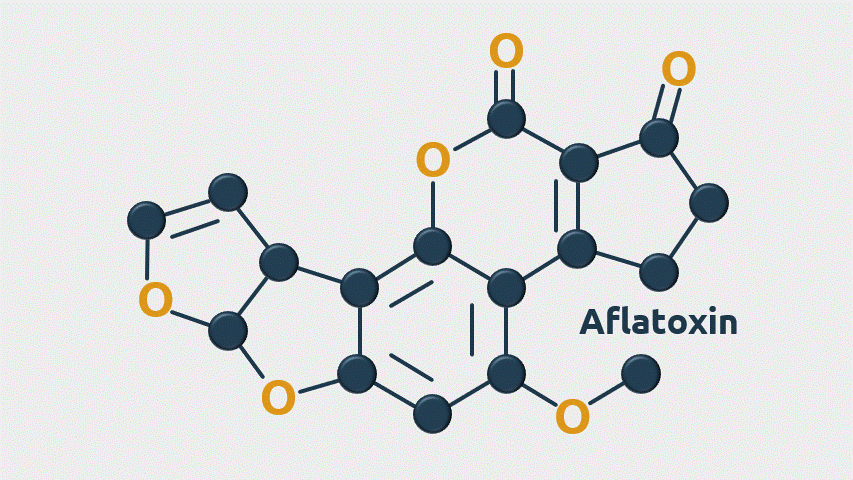
When stressed, Aspergillus produces many types of metabolites (14 known). The most harmful mycotoxins include aflatoxins M1, M2, B1, B2, G1, and G2—B1 is carcinogenic. These mycotoxins inhibit DNA and RNA synthesis (by binding to DNA and proteins to prevent transcription), reduce enzyme activity, and decrease immune cell development. This results in hepatotoxicity, reduced lipid digestion, decreased renal function, and immune depression. The toxin’s target organs are the liver and immune system, but reactions differ by species.
Observable symptoms include:
This toxin is unique as it is a risk to both feed and food. Aflatoxin M1 is a transformation of aflatoxin B1 and can be absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract of a ruminant and found in milk. Most parts of the developed world test for aflatoxin M1 in milk and will dump anything over 500 ppt/0.05 ppb.
EU aflatoxin in feed legislation
| All feed materials | 0.02 ppm |
| Raw ingredient Cattle/sheep/goats | 0.02 ppm |
| Raw ingredient dairy animals | 0.005 ppm |
| Raw ingredient calves and lambs | 0.01 ppm |
| Raw ingredient pigs and poultry | 0.02 ppm |
| Complete feedstuffs | 0.01 ppm |
United States aflatoxin in feed legislation
| All feed materials | |
| Cottonseed for cattle/swine/poultry | 300 ppb |
| Corn and peanuts for swine | 200 ppb |
| Corn and peanuts for breeding cattle/swine/poultry | 100 ppb |
| Corn, peanuts for young animals | 20 ppb |
| Dairy cattle and other species Milk |
20 ppb 0.5 ppb |
Would you like to be kept informed of our latest developments? Register here and stay up to date.
"*" indicates required fields
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
